T cell ELISPOT assay
Monkey ELISPOT kits are validated for Old World monkeys (e.g. rhesus macaques, pig-tailed macaques, cynomolgous monkeys and baboons) and New World monkeys (marmosets).
Our FluoroSpot kits detect two cytokines from a single T cell using fluorescent-labeled antibodies.
Intended use of the T cell ELISPOT assay
The ELISPOT assay is highly sensitive method for detecting cytokine-secreting cells at the single cell level. The ELISPOT can be performed in cell suspensions from blood (PBMC), lymphoid tissue, spleen, bone marrow, or CNS tissue.
Unlike mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR) and Cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) assays, or RT-PCR analysis, ELISPOT assays avoids radioactivity, and detects secreted proteins (not mRNA).
The sensitivity of the ELISPOT assay surpasses ELISA and intracellular cytokine staining1-3 by the plate-bound antibodies capturing proteins immediately upon secretion, enabling detection of rare cells (as few as 1/100,000).
Application
-
The ELISPOT assay is a powerful tool for monitoring disease progression. It detects shifts in cytokine producing cells across body tissue, which reflect changes in immune function4 making it valuable for both human and animal studies.
-
The ELISPOT assay is valuable for studying how new viruses affect the immune system and for early vaccine development. It was notably used during the COVID-19 pandemic to assess T cell responses to SARS-CoV-2.5,6
-
The ELISPOT assay has been shown significant promise in predicting allograft rejection in organ transplantation.7
-
The ELISPOT assay is widely used to determine the frequency of antigen-specific T cell responses in PBMC of vaccinated non-human primates8,9 and spleen cells of immunized rats10 and mice11.
-
The ELISPOT assay may help reveal how pathogens escape immune protection.12
-
The ELISPOT assay has been used in the vaccine trials to detect tumor-specific T cells.13,14
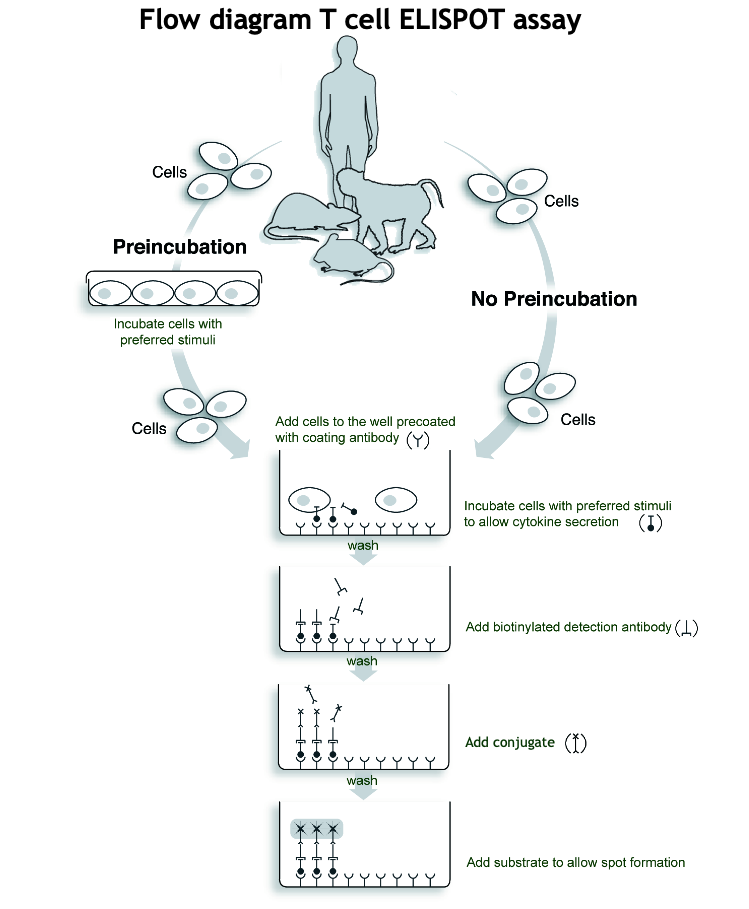
Brief description of the T cell ELISPOT procedure
In ELISPOT, cells are incubated in antibody-coated wells where secreted cytokines bind.
After washing away the cells, captured cytokine are detected using biotinylated antibodies and enzyme-labeled streptavidin.
A substrate is added, forming colored spots that mark cytokine secretion sites.
The different steps of the T cell ELISPOT procedure are illustrated in the T cell ELISPOT assay Flow diagram.
Example of the Human T cell ELISPOT assay:
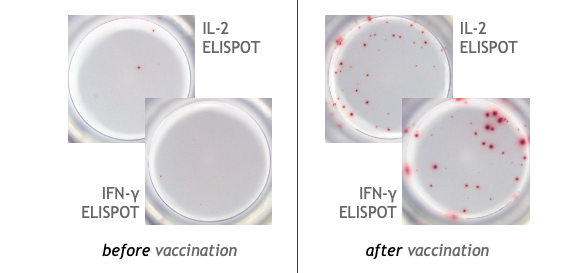
This is an example of IFN-γ and IL-2 specific spots produced by T cells in human PBMC.
PBMC from a COVID-19 mRNA booster-vaccinated individual were stimulated with a SARS-CoV-2 peptide pool and incubated for 24 hours on the ELISPOT plate (2x105 cells/well) to detect IFN-γ and IL-2 secretion.
U-CyTech ELISPOT products
Follow these links to go to directly to our:
- Human ELISPOT products
- Monkey ELISPOT products
- Marmoset ELISPOT products
- Mouse ELISPOT products
- Rat ELISPOT product
References
- Tanguay S and Killion JJ (1994). Direct comparison of ELISPOT and ELISA-based assays for detection of individual cytokine-secreting cells. Lymphokine Cytokine Res. 13: 259-63.
- Carter LL and Swain SL (1997). Single cell analyses of cytokine production. Curr. Opin Immunol. 9: 177-82.
- Herold KC et al. (2009). Validity and reproducibility of measurement of islet autoreactivity by T-cell assays in subjects with early type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 58: 2588-95.
- Van der Meide PH et al. (1998). Discontinuation of treatment with IFN-beta leads to exacerbation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats. Rapid reversal of the antiproliferative activity of IFN-beta and excessive expansion of autoreactive T cells as disease promoting mechanisms. J. Neuroimmunol. 84:14-23.
- U-CyTech products used in this study:
- Zhao B et al. (2021). Alterations in Phenotypes and Responses of T Cells Within 6 Months of Recovery from COVID-19: A Cohort Study. Virol. Sin. Oct;36(5): 859-868
- U-CyTech products used in this study:
- Feng L et al. (2020). An adenovirus-vectored COVID-19 vaccine confers protection from SARS-COV-2 challenge in rhesus macaques. Nat Commun. 11: 4207.
- U-CyTech products used in this study:
- Monkey species: Macaca mulatta
- Mendoza Rojas A et al. (2023). Alloreactive T cells to Assess Acute Rejection Risk in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transplant Direct. 9(5): e1478.
- U-CyTech products used in this study:
- Rollier CS et al. (2016). T- and B-cell responses to multivalent prime-boost DNA and viral vectored vaccine combinations against hepatitis C virus in non-human primates. Gene Ther. 23: 753-759.
- U-CyTech products used in this study:
- Monkey species: Macaca mulatta
- Karmakar S et al. (2014). Cross-species protection: Schistosoma mansoni Sm-p80 vaccine confers protection against Schistosoma haematobium in hamsters and baboons. Vaccine 32: 1296-303.
- U-CyTech products used in this study:
- Monkey species: Papio anubis
- Liu GX et al. (2009). Mucosal and systemic immunization with targeted fusion anti-caries DNA plasmid in young rats. Vaccine 27: 2940-7.
- U-CyTech products used in this study:
- Liu X et al. (2023). A mosaic influenza virus-like particles vaccine provides broad humoral and cellular immune responses against influenza A viruses. NPJ vaccines. 8(1): 132.
- U-CyTech products used in this study:
- Li Z et al. (2022). Impaired T lymphocyte responses during childhood Staphylococcus aureus infection. J. Infect. Dis. 225: 177-85.
- U-CyTech products used in this study:
- Mirandola L et al. (2019). A novel method for efficient generation of antigen-specific effector T-cells using dendritic cells transduced with recombinant adeno-associated virus and p38 kinase blockade. J. Transliterates. Med. 17: 424.
- U-CyTech products used in this study:
- Peng S et al. (2022) Combination neoantigen-based dendritic cell vaccination and adoptive T-cell transfer induces antitumor responses against recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Res. 10(6): 728-744.
- U-CyTech products used in this study: