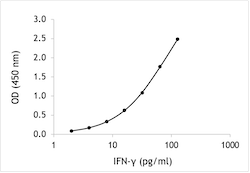
Human interferon-gamma ELISA:
Assay range: 2-128 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 2 pg/ml
Specificity: nat. and rec. human IFN-gamma
Calibration: rec. human IFN-gamma
Type of sample: serum, plasma, culture supernatant
Assay range: 2-128 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 2 pg/ml
Specificity: nat. and rec. human IFN-gamma
Calibration: rec. human IFN-gamma
Type of sample: serum, plasma, culture supernatant
Catalogue Number
CT201A
Description
Human IFN-γ ELISA kit - 5-plate
Price
€ 530.00
Contents
- coating antibody
- biotinylated detection antibody
- Cytokine standard (5x)
- Streptavidin-HRP conjugate
- TMB substrate solution
- Stop solution
- Cytokine stabilization buffer (CSB)
- BSA stock solution (10%)
- Tween-20
- ELISA plates with cover slips
References list
- C-Terminal PEGylation Improves SAAP-148 Peptide's Immunomodulatory Activities.
- Induction of M-MDSCs with IL6/GM-CSF from adherence monocytes and inhibition by WP1066.
- Effect of inhaled anaesthetics gases on cytokines and oxidative stress alterations for the staff health status in hospitals.
- Infection with a virus generates a polyclonal immune response with broad alloreactive potential.
- Retinoic acid primes human dendritic cells to induce gut-homing, IL-10-producing regulatory T cells.
- CD39 is involved in mediating suppression by Mycobacterium bovis BCG-activated human CD8(+) CD39(+) regulatory T cells.
- Identification of AKAP-4 as a new cancer/testis antigen for detection and immunotherapy of prostate cancer.
- Vaccine-induced allo-HLA-reactive memory T cells in a kidney transplantation candidate.
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis peptides presented by HLA-E molecules are targets for human CD8 T-cells with cytotoxic as well as regulatory activity.
- Hepatitis B virus surface antigen impairs myeloid dendritic cell function: a possible immune escape mechanism of hepatitis B virus.
- Superior immunomodulatory effects of intravenous immunoglobulins on human T-cells and dendritic cells: comparison to calcineurin inhibitors.
- Immunological crossreactivity of the Mycobacterium leprae CFP-10 with its homologue in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- IL-12 receptor deficiency revisited: IL-23-mediated signaling is also impaired in human genetic IL-12 receptor beta1 deficiency.
- Divergent role for TNF-alpha in IFN-gamma-induced killing of Toxoplasma gondii and Salmonella typhimurium contributes to selective susceptibility of patients with partial IFN-gamma receptor 1 deficiency.
- Detection of active tuberculosis infection by T cell responses to early-secreted antigenic target 6-kDa protein and culture filtrate protein 10.



